Today, I’m going to break down how annuity cap and participation rates work, using a simple options budget example. This is crucial for anyone looking to make informed decisions about their retirement strategy.
How Options Budgets Set Annuity Cap and Participation Rates
First, let’s get a grasp on the options budget. Imagine an annuity company earning a 5% return from investment-grade bonds. They use 2% for operating costs and profit, leaving 3% for enhancing client growth opportunities. This leftover percentage is key in setting caps and participation rates.
Remember: The company’s profit doesn’t hinge on this budget or index performance. Their goal is to offer you the best growth options amid intense competition.
Your Choices: Guaranteed Return or Index Tracking
You’re presented with two choices: lock in a 3% guaranteed return or aim for potentially higher gains by tracking an index. This example shows a crediting strategy that is offered annually. Keep in mind, that this is just an example for educational purposes, especially with current fluctuating interest rates.
The Nuts and Bolts: Buying and Selling Call Options
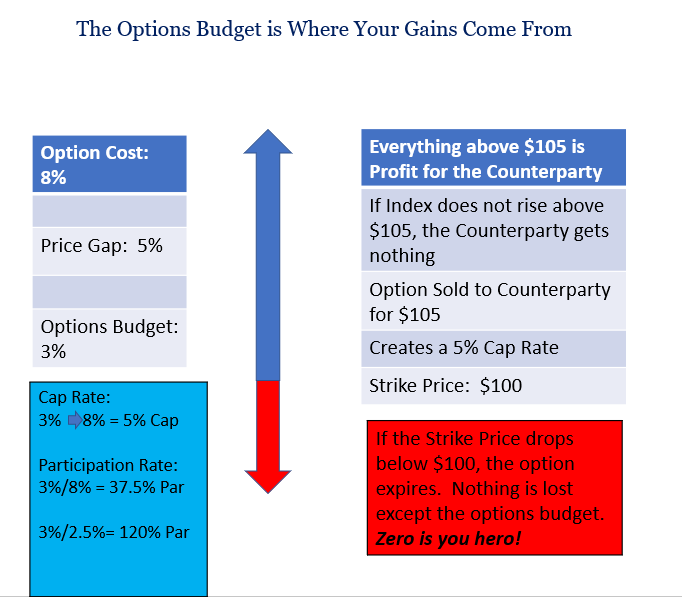
Let’s dive deeper. Say the company has a $3 budget to buy call options for every $100 of premium. If a call option costs $8, they can’t just overspend; that’s not sustainable. So, they buy the $8 call option and then sell a second call option for $5 to balance the budget. This involves a concept called the ‘strike price’, which is essentially the starting point of the index’s value.
In our scenario, the company’s original call option profits from anything above 100. To recoup the $5, they sell another option with a strike price of 105. This sets the cap rate.
Cap Rates and Participation Rates: How They Work
In this setup, if the index value rises between 100 and 105 over a year, you get the full value increase. Anything above 105 goes to the counterparty. Interestingly, in such a scenario, the annuity company gains nothing from this call option strategy.
The same principle applies to participation rates. They are calculated by dividing the options budget by the option cost. So, in a situation where the index rises by 10%, and your participation rate is 37.5%, you’d gain 3.75%.
Choosing Indexes: Volatility vs. Stability
Indexes with higher volatility generally offer lower caps and participation rates, and vice versa. It’s worth considering alternative, less volatile indexes for potentially higher rates and more consistent returns.
The Unique Advantage of Fixed Indexed Annuities (FIAs)
FIAs offer a blend of upside potential and downside protection that’s hard to find elsewhere. They’re based on sophisticated investment strategies that are typically beyond individual capabilities, especially when considering the risks involved.
Understanding Renewal Rates
It’s important to note that caps and participation rates are subject to change due to varying option costs over time. Some companies might offer high rates now but can’t sustain them long-term. It’s essential to consider the likelihood of rate stability throughout the term of your annuity. The best way to do that is by working with an annuity expert who deals with these companies regularly.
Recap and Resources
To sum up, annuity companies use their options budget to provide growth opportunities through cap rates and participation rates. The volatility of the chosen index plays a significant role in determining these rates. Remember, you don’t need to understand all these details to benefit from FIAs, but it’s good to have a basic understanding.
SEC Bulletin on Index Annuity Cap Rates & Return Rates
